If you’ve ever dealt with suppliers or manufacturers, you’ve likely come across the term “MOQ.”
But what exactly does it mean, and why is it so important for businesses? That’s exactly what we’ll cover today.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about MOQ including why it matters, how it works for both buyers and suppliers.
Let’s jump right into it!
What Is the Meaning of MOQ?
An MOQ stands for Minimum Order Quantity. While the abbreviation may be self-explanatory for most people, we’ll explain it for the sake of clarity.
MOQ is the minimum number of products that you must purchase from a supplier in order for the transaction to be processed.
MOQ is a term that is generally used in businesses. This term is especially used in large-scale business models such as B2B where a manufacturer or a supplier arranges or manufactures products in higher quantities and sells them to another business.
Most sellers in the B2B model work on MOQs as this is different from a retail or B2C model where sellers sell as low as one piece to buyers.
MOQs can be expressed in different units, depending on the product type, such as:
- Pieces
- Sets
- Boxes
- Pairs
- Kilograms
- Square meters
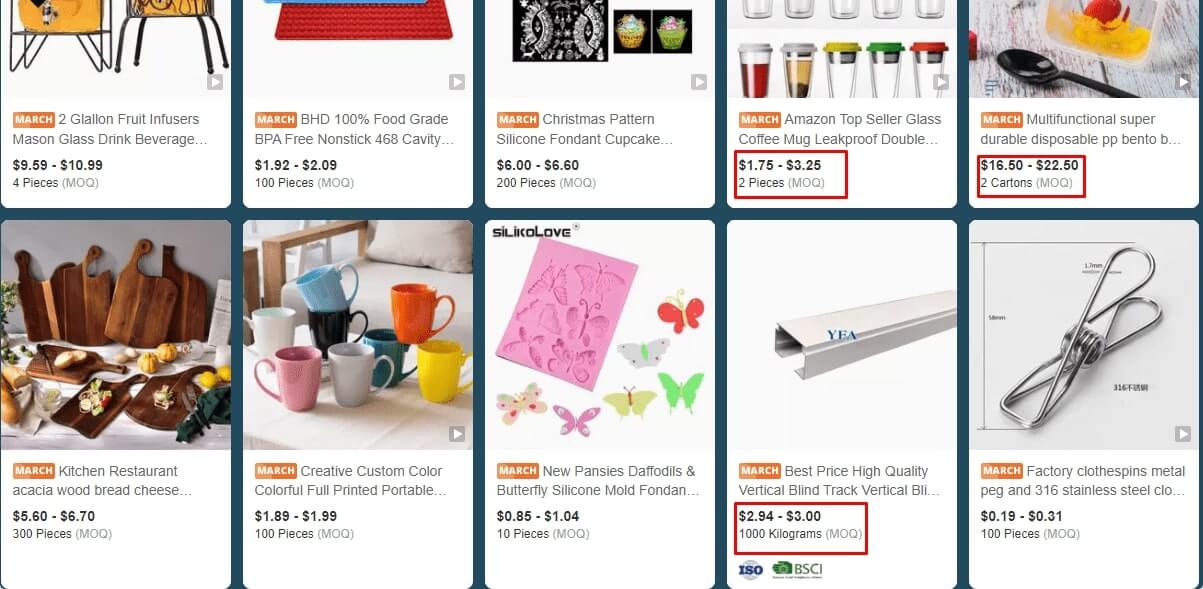
You will also find suppliers who would ask you to spend a minimum amount for an order to be processed. For example, you would have to place an order of above $100 for a purchase to happen.
Examples of MOQ
To better understand how MOQs work in real-world scenarios, let’s look at a few examples across different industries:
- Clothing Manufacturer – A factory producing t-shirts might set an MOQ of 500 pieces per design and color. This means you need to order at least 500 t-shirts of the same design and color to meet their requirement.
- Electronics Supplier – For a supplier selling mobile phone accessories, the MOQ might be 1,000 units per item. If you’re interested in phone cases, you’d need to order 1,000 cases of a specific model or design.
- Furniture Wholesale – A furniture supplier might require an MOQ of 50 pieces per item or design, whether it’s chairs, tables, or sofas.
- Raw Materials – In industries like textiles, an MOQ might be based on weight. For instance, a fabric supplier could require a minimum order of 500 kilograms per color.
- Custom Products – If you’re ordering a product with your branding or custom specifications, suppliers often set higher MOQs due to the added production complexity. For instance, a private label skincare manufacturer might set an MOQ of 10,000 units per formula.
What Does Low MOQ Mean?
A low MOQ means a lower number of items or pieces per order. Buyers are not always interested in buying larger quantities at once.
Some businesses work on a small scale and require low amounts of orders as opposed to other businesses that work on larger scales where low MOQ does not suit.
A low MOQ incurs additional costs per item. Larger MOQs come with smaller costs per item. Businesses that are in the early stage of development generally prefer low MOQs.
This may be because they just want to check if the products work out for them or not. Such businesses are in search of suppliers who are ready to either sell with low MOQs or are willing to negotiate the MOQs as per their request.
This is where the manufacturers or suppliers who sell in segments come in. A supplier who has manufactured 1000 pieces of a product may be selling to 10 businesses with 100 MOQ per order.
Note that some suppliers offer different MOQ ranges and adjust the price based on that. For example, 0-99, 100-499, 500-1,000 pieces and so on.
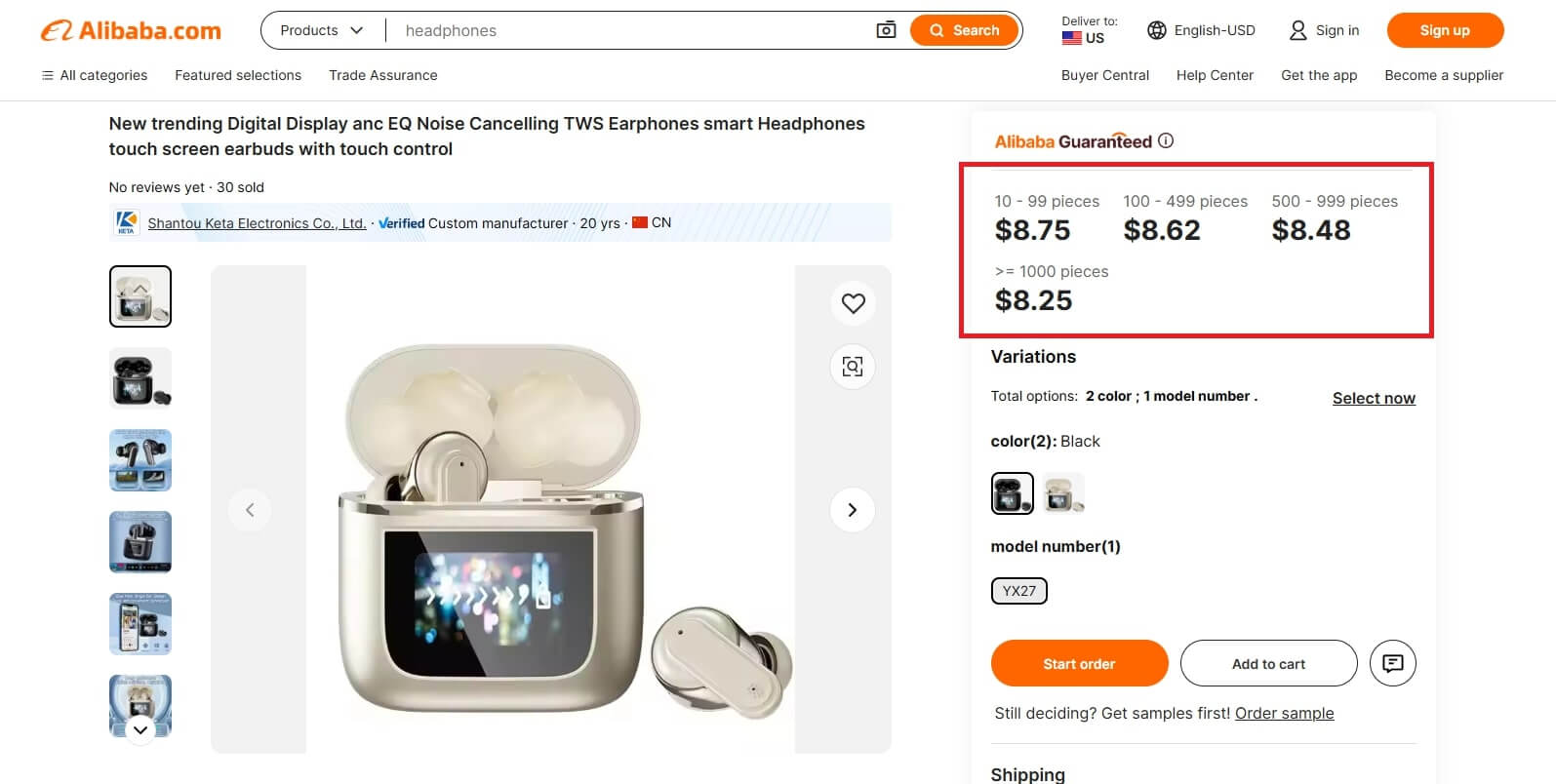
In this way, the supplier will also get rid of his manufactured stock, and businesses that prefer smaller MOQs are also accommodated. So, it’s like a win-win situation for both.
How to Calculate Minimum Order Quantity?
Calculating the Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) involves balancing production costs, profitability, and customer demand. For suppliers, this calculation is key to ensuring that they remain competitive while covering their operational expenses. Here’s how MOQs are typically determined:
Assess Production Costs

The first step is to evaluate the total cost of production, including:
- Raw materials
- Labor
- Machinery or equipment costs
- Overheads (e.g., utilities, rent, and maintenance)
Understanding these expenses helps determine the minimum quantity required to produce goods at a break-even point.
Consider Demand and Market Trends
Suppliers must align their MOQs with market demand. For example, setting a high MOQ in a niche market with limited buyers may discourage potential customers, while a low MOQ in a high-demand market could strain production capacity.
Factor in Profit Margins

A supplier needs to ensure that each unit sold contributes to profitability. They calculate the MOQ by dividing the desired profit margin by the cost per unit and ensuring the order size is large enough to meet that threshold.
Account for Inventory Management
MOQ should reflect the supplier’s ability to store and manage inventory. For instance, if producing a large batch leads to excess stock that can’t be stored or sold within a reasonable timeframe, the MOQ may need to be adjusted.
Include Shipping and Logistics Costs
Shipping costs are often a significant factor, especially for international suppliers. Combining these costs with production expenses ensures the MOQ covers all related charges.
Use the Formula (If Applicable)

A simple formula often used for calculating MOQ is:
MOQ = (Total Production Cost + Desired Profit) ÷ Unit Price
Example:
If the total production cost is $1,000, the desired profit is $500, and the unit price is $10, then:
MOQ = ($1,000 + $500) ÷ $10
MOQ = $1,500 ÷ $10
MOQ = 150 units
For buyers, understanding this calculation can aid in negotiations and planning bulk purchases effectively.
What Are the Pros and Cons of MOQ for Suppliers and Customers?
For suppliers, setting a Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) is a strategic decision that can influence sales, production efficiency, and long-term partnerships.
While MOQs offer the potential for increased profitability and smoother operations, they also come with their own set of challenges.
In the section below, we explore the advantages and disadvantages of MOQ from the supplier’s perspective first to help you understand the impact it can have on your business.

Pros of MOQ for Suppliers
- Supports Mass Production: Simplifies manufacturing by producing in bulk, which reduces costs and improves efficiency.
- Streamlines Large-Scale Sales: Encourages bulk orders, reducing the hassle of managing numerous small transactions.
- Facilitates Efficient Shipping: Enables streamlined shipment in uniform batches, making logistics more manageable.
- Builds Long-Term Relationships: Helps build steady relationships with bulk buyers, wholesalers, and stockists.
Cons of MOQ for Suppliers
- Limits Buyer Pool: Attracts fewer customers as only businesses or bulk buyers are interested.
- Excludes Consumer Sales: Reduces opportunities to engage directly with end users, resulting in zero consumer sales.
- Lower Margins Per Unit: Bulk sales often come with lower profit margins compared to retail pricing in the B2C model.
- Requirement for Samples: Buyers demand samples before committing to large orders, creating extra effort for suppliers.
MOQ can be a double-edged sword for buyers, offering unique advantages while also presenting certain challenges. On the one hand, it supports cost efficiency and streamlined operations.
On the other, it demands careful planning and resource allocation to avoid potential pitfalls.
Below, we’ve outlined the key pros and cons of MOQ for buyers to help you evaluate its impact on your business decisions.

Pros of MOQ for Buyers
- Special Pricing: Bulk orders often come with lower prices per unit compared to retail.
- Efficient Stock Management: Helps maintain consistent inventory levels, supporting regular sales and customer trust.
- Prevents Stock Shortages: Ensures steady product availability, reducing the risk of running out of stock.
- Promotional Campaigns: Enables the launch of sales or promotional events with surplus stock.
- Competitive Pricing Advantage: Allows for price reductions to outcompete rivals while remaining profitable.
- Cross-Selling Potential: Attracts customers for promoted products and encourages purchases of other items.
Cons of MOQ for Buyers
- High Initial Investment: Smaller businesses may struggle to allocate capital for large MOQ purchases.
- Operational Strain: Managing larger inventories requires additional resources, such as staff and storage.
- Higher Maintenance Costs: Increased expenses for warehousing, product care, and damage prevention.
- Reduced Product Variety: Limits the ability to test and diversify product offerings.
- Missed Opportunities: Ties up capital, potentially causing missed chances to invest in trending or seasonal items.
FAQs
What Is the Average MOQ for a New Product?
The average MOQ for a new product can vary widely depending on the supplier, product type, and industry. Typically, suppliers set MOQs ranging from 50 to 500 units for new products.
However, niche or high-value items might have higher MOQs. It’s always a good idea to ask suppliers for their specific MOQ requirements for new products and negotiate if needed.
Can I Get a Lower MOQ if I’m Just Starting a Business?
Yes, many suppliers are open to negotiating a lower MOQ for new businesses, especially if you can prove your commitment to growing a long-term business relationship.
However, keep in mind that the price per unit may be higher for smaller orders since suppliers often offer discounts for larger bulk orders.
How Does MOQ Impact My Pricing?
MOQ directly affects pricing. Typically, the higher the quantity you order, the lower the price per unit. Suppliers offer bulk discounts to encourage larger orders and reduce their production and shipping costs.
If you are required to meet an MOQ but only need a smaller quantity, your cost per unit might be higher compared to buying larger quantities.
What Is the Purpose of MOQ in the Supply Chain?
The purpose of MOQ in the supply chain is to make sure that production and distribution remain efficient and cost-effective.
By setting a minimum order, suppliers can maintain stable production runs, reduce waste, and optimize their resources.
MOQs also help suppliers maintain profitability by ensuring they are not selling in smaller quantities that would reduce their margins.
Summary
MOQs are a standard part of many businesses, especially those dealing with large-scale orders.
Understanding how they work is essential for both buyers and sellers to make informed decisions and avoid any surprises down the line.
At NicheDropshipping, we understand that meeting MOQs can be challenging.
That’s why we help businesses find the products they need, even with low or no MOQ requirements.
Whether you’re just starting or scaling up, we’ve got you covered. If you’re ready to make sourcing easier and more cost-effective, contact us and our expert agents will guide you!

